DevOps
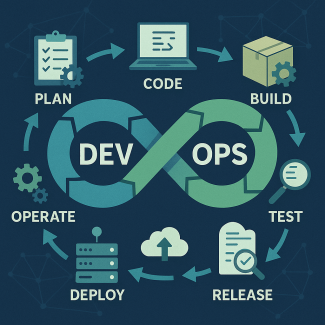
DevOps is a combination of methodologies, tools, and culture aimed at shortening the development cycle—from the initial planning stage all the way to the final software deployment. DevOps enables organizations to accelerate their development processes and improve the quality of results by enhancing planning, coding, building, testing, monitoring, and support workflows.
As part of the DevOps approach, we use automated tools that allow us to deploy fixes and add new features rapidly, while ensuring these changes don’t negatively impact the existing application. These tools give us full control over the process, enabling us to track every software change and roll back if needed.
The DevOps culture fosters full collaboration between different teams—developers, support staff, and operations—allowing each group to be involved at every stage of the process. This leads to rapid idea sharing and instills a shared sense of responsibility for the quality and stability of the final product.
In fact, DevOps is more than just a methodology; it’s a culture of collaboration that merges development (Dev) and operations (Ops) into a unified process. This approach helps organizations deliver software faster, with higher quality and lower costs. Combining these processes enables organizations to respond flexibly and quickly to change, while maintaining the highest standards of security and performance.
Two core components in the DevOps world are CI/CD and architecture, and their importance cannot be overstated.
CI (Continuous Integration) is a process where new code is continuously merged into the existing codebase. The CI system runs automated tests every time new code is added, allowing the development team to quickly detect and fix any issues caused by changes.
CD (Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment) is the next step. Continuous Delivery means the new code is always ready to be released at any time. Continuous Deployment goes further by automatically releasing the changes directly to the customer.
Architecture also plays a critical role in DevOps. Software architecture defines the overall system structure, including its key components and their interactions. When designing the architecture, factors such as stability, performance, maintainability, and security are taken into account.
In DevOps, microservices architecture is a popular way to build systems. Instead of creating a large monolithic codebase, the system is divided into small, independent services that communicate with each other. Each service can be developed, tested, deployed, and operated independently.
The combination of CI/CD and microservices architecture allows organizations to be more agile and responsive to changes.